全栈数据流
¥Fullstack Data Flow
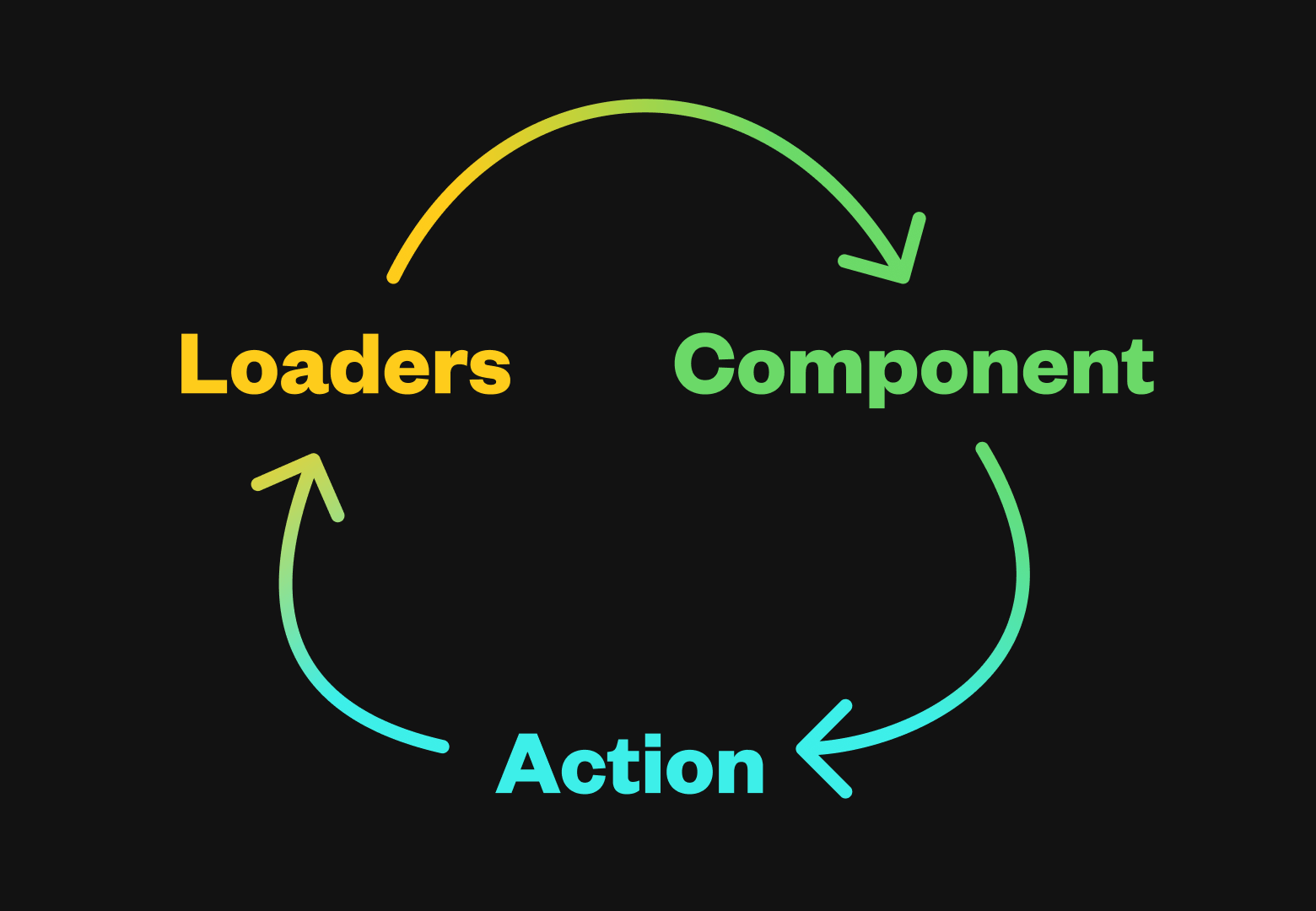
Remix 的主要功能之一是它能够自动保持 UI 与持久服务器状态同步。它分为三个步骤:
¥One of the primary features of Remix is the way it automatically keeps your UI in sync with persistent server state. It happens in three steps:
-
路由加载器向 UI 提供数据
¥Route loaders provide data to the UI
-
表单将数据发布到路由操作,从而更新持久状态。
¥Forms post data to route actions that update persistent state
-
页面上的加载器数据会自动重新验证
¥Loader data on the page is automatically revalidated
路由模块导出
¥Route Module Exports
我们来考虑一个用户账户编辑路由。路由模块有三个导出,我们将逐一介绍并讨论:
¥Let's consider a user account edit route. The route module has three exports that we'll fill in and talk about:
export async function loader() {
// provides data to the component
}
export default function Component() {
// renders the UI
}
export async function action() {
// updates persistent data
}
路由加载器
¥Route Loader
路由文件可以导出一个 loader 函数,该函数向路由组件提供数据。当用户导航至匹配的路由时,数据将首先加载,然后页面将被渲染。
¥Route files can export a loader function that provides data to the route component. When the user navigates to a matching route, the data is first loaded and then the page is rendered.
import type { LoaderFunctionArgs } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
import { json } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
export async function loader({
request,
}: LoaderFunctionArgs) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return json({
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
});
}
export default function Component() {
// ...
}
export async function action() {
// ...
}
路由组件
¥Route Component
路由文件的默认导出是渲染的组件。它使用 useLoaderData 读取加载器数据:
¥The default export of the route file is the component that renders. It reads the loader data with useLoaderData:
import type { LoaderFunctionArgs } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
import { json } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
import { useLoaderData, Form } from "@remix-run/react";
export async function loader({
request,
}: LoaderFunctionArgs) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return json({
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
});
}
export default function Component() {
const user = useLoaderData<typeof loader>();
return (
<Form method="post" action="/account">
<h1>Settings for {user.displayName}</h1>
<input
name="displayName"
defaultValue={user.displayName}
/>
<input name="email" defaultValue={user.email} />
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</Form>
);
}
export async function action() {
// ...
}
路由操作
¥Route Action
最后,提交表单时,将调用与表单 action 属性匹配的路由上的操作。在本例中,它们是相同的路由。表单字段中的值将通过标准 request.formData() API 提供。请注意,输入中的 name 属性与 formData.get(fieldName) getter 耦合。
¥Finally, the action on the route matching the form's action attribute is called when the form is submitted. In this example it's the same route. The values in the form fields will be available on the standard request.formData() API. Note the name attribute on the inputs is coupled to the formData.get(fieldName) getter.
import type {
ActionFunctionArgs,
LoaderFunctionArgs,
} from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
import { json } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
import { useLoaderData, Form } from "@remix-run/react";
export async function loader({
request,
}: LoaderFunctionArgs) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return json({
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
});
}
export default function Component() {
const user = useLoaderData<typeof loader>();
return (
<Form method="post" action="/account">
<h1>Settings for {user.displayName}</h1>
<input
name="displayName"
defaultValue={user.displayName}
/>
<input name="email" defaultValue={user.email} />
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</Form>
);
}
export async function action({
request,
}: ActionFunctionArgs) {
const formData = await request.formData();
const user = await getUser(request);
await updateUser(user.id, {
email: formData.get("email"),
displayName: formData.get("displayName"),
});
return json({ ok: true });
}
提交和重新验证
¥Submission and Revalidation
当用户提交表单时:
¥When the user submits the form:
-
Remix 通过
fetch将表单数据发送到路由操作,待处理状态则通过useNavigation和useFetcher等钩子变为可用状态。¥Remix sends the form data to the route action via
fetchand pending states become available through hooks likeuseNavigationanduseFetcher. -
操作完成后,将重新验证加载器以获取新的服务器状态。
¥After the action completes, loaders are revalidated to get the new server state.
-
useLoaderData从服务器返回更新后的值,待处理状态返回空闲状态。¥
useLoaderDatareturns the updated values from the server and the pending states go back to idle.
这样,UI 便与服务器状态保持同步,而无需编写任何同步代码。
¥In this way, the UI is kept in sync with server state without writing any code for that synchronization.
除了 HTML 表单元素之外,还有多种提交表单的方式(例如响应拖放操作或 onChange 事件)。关于表单验证、错误处理、待处理状态等,还有很多内容需要讨论。我们稍后会详细介绍,但以上是 Remix 数据流的要点。
¥There are various ways to submit a form besides an HTML form element (like in response to drag and drop, or an onChange event). There is also a lot more to talk about around form validation, error handling, pending states, etc. We'll get to all of that later, but this is the gist of data flow in Remix.
JavaScript 加载前
¥Before JavaScript Loads
从服务器发送 HTML 时,最好在 JavaScript 加载之前就让它工作。Remix 中的典型数据流会自动执行此操作。流程相同,但浏览器会执行部分工作。
¥When you send HTML from the server, it's best to have it work even before JavaScript loads. Typical data flows in Remix do this automatically. The flow is the same, but the browser does some of the work.
当用户在 JavaScript 加载之前提交表单时:
¥When the user submits the form before JavaScript loads:
-
浏览器将表单提交给操作(而不是
fetch),并且浏览器的待处理状态激活(旋转的图标)。¥The browser submits the form to the action (instead of
fetch) and the browsers' pending states activate (spinning favicon) -
操作完成后,将调用加载器
¥After the action completes, loaders are called
-
Remix 渲染页面并将 HTML 发送到浏览器
¥Remix renders the page and sends HTML to the browser